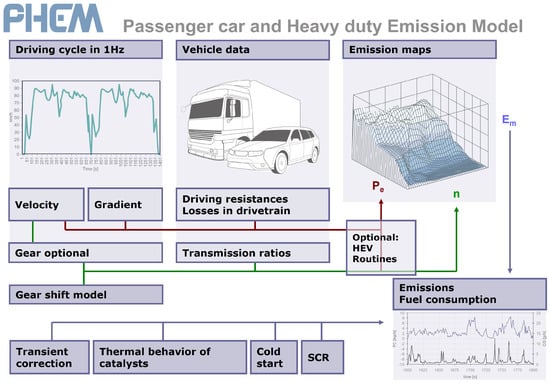
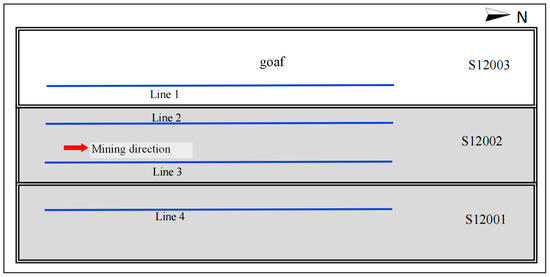
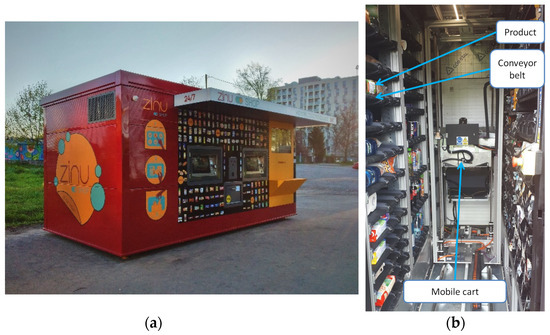
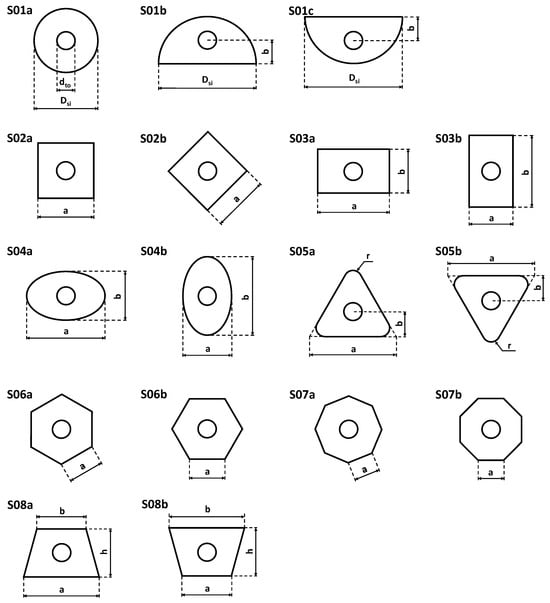
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Issues
A topical collection in Energies (ISSN 1996-1073). This collection belongs to the section "B: Energy and Environment".
Viewed by 45369Editors
Interests: environmental protection processes and devices; water and wastewater treatment; sewage sludge to energy; energy consumption in sewage sludge treatment; flue gas cleaning; modelling of power systems; clean energy systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: design and operation of machines and equipment in renewable energy and environmental protection; use of numerical methods in modelling machinery and equipment operation; validation and reliability of obtained results; modelling wind turbines; settlers; modelling fluid flow; multiphase systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: waste to energy processes; sewage sludge to energy; fluid mechanics; modern power systems; decarbonisation; climate protection
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Energy harvesting is one of the primary activities of society today, necessary not only for our development, but also for our survival. Each industrial process, economy and individual household requires access to a source of energy, which is mainly electricity. Since the Industrial Revolution, we primarily obtain energy by burning fossil fuels. This applies to both large industrial plants and smaller business entities, and even most individual farms that are connected to electricity or heating networks. Unfortunately, using fossil fuels for energy has a significant negative impact on the environment. The emission of large CO2 loads cause substantial climate changes, while the emission of other gaseous pollutants, the environmental degradation related to the acquisition of these fuels, and even the management of post-process waste are also problems. Another equally important aspect of the use of fossil fuels is the unstable economic situation caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as current political events in Europe and across the world. These issues cause a significant increase in interest in using energy other than fossil energy sources. The problems mentioned above significantly translate into significant increases in the prices of energy and its carriers. The most effective way to ensure the energy supply and change its negative environmental impact is to avoid unnecessary consumption. Hence, it is very important to search for ways to increase the energy efficiency of all processes related to the harvesting and processing of primary energy carriers. With huge volumes of energy being processed/consumed, even a slight improvement in energy efficiency in the energy processing chain will bring about significant effects in the form of energy savings and a substantial reduction in climate impact. Optimisation of the processes for obtaining and processing energy is, therefore, not a scientific or engineering curiosity, but it is a significant way to at least partially solve the problems related to the energy crisis. Improving, at the same time, the efficiency of the processes that obtain energy and the processes that consume energy will allow for the development of technology, which provides an excellent opportunity to reduce our harmful impacts on the environment, from the use of energy sources to consumer utility devices.
The legislation of many countries and international institutions, such as the European Union, currently considers the environmental impact of energy conversion. Examples of such efforts include, for example, the EU Energy Efficiency Directive (2012/27 UE) and a document entitled "The European Green Deal", a part (extension) of which is the "Fit for 55" package. One of the leading lines of action in the Fit for 55 package is the increase in energy efficiency.
Increasing energy efficiency can and should be sought out through the optimisation of energy processes, the construction and insulation of buildings or structures, and the machine operation regime (after all, by definition, the operation of each machine is related to energy conversion). In other words, an improvement in energy efficiency applies to almost all aspects of the functioning of society: from mineral extraction plants; through all manufacturing, municipal and processing processes; to all aspects of people's everyday activities. In every aspect of human activity, the energy efficiency of the processes and devices used can be improved.
These problems mentioned above are the main themes of this Topical Collection of Energies.
Prof. Dr. Marian Banaś
Prof. Dr. Krzysztof Kołodziejczyk
Prof. Dr. Tadeusz Paja̧k
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- energy
- primary energy
- energy efficiency
- energy consumption
- reducing energy consumption
- energy economics and policy
- circular economy in renewable energy
- energy sources and recourses
- energy harvesting
- combustion
- energy conversion
- energy storage
- energy recovering
- pollutant emissions
- emission reduction
- climate change
- greenhouse gas
- decarbonisation
- carbon capture, utilisation and storage
- clean energy
- fossil fuel
- alternative fuel
- biomass
- solar
- wind
- tidal
- geothermal
- fuel cells
- hydrogen
- municipal solid wastes
- waste to energy
- EU Energy Package
- fit for 55 package