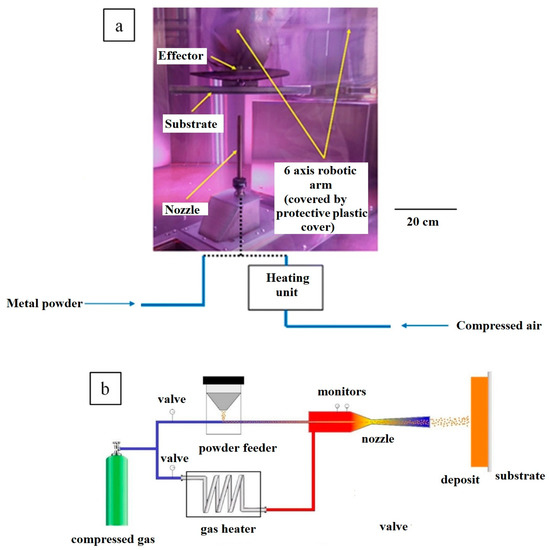
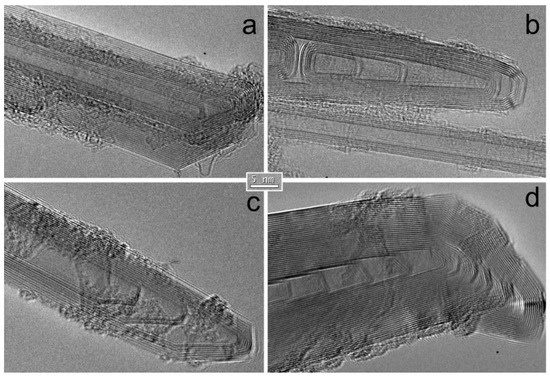
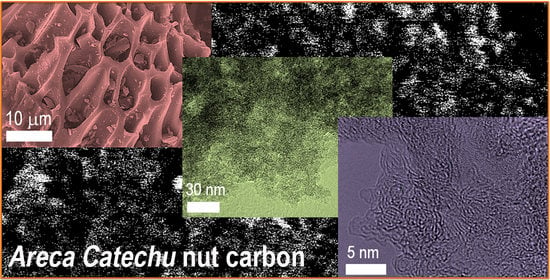
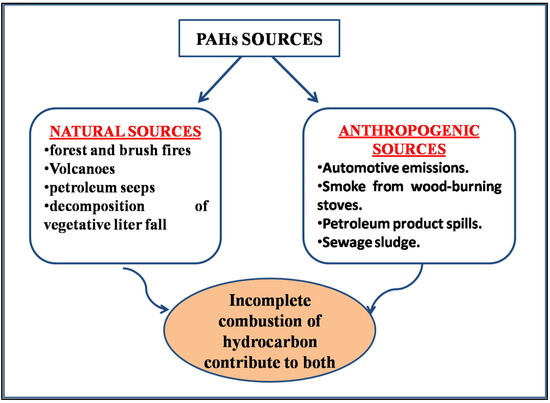
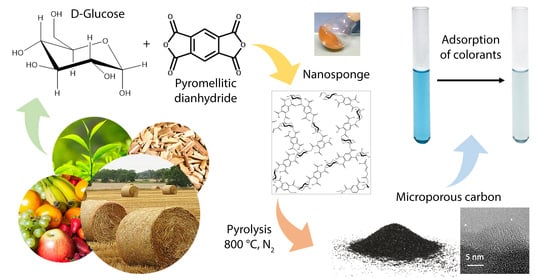
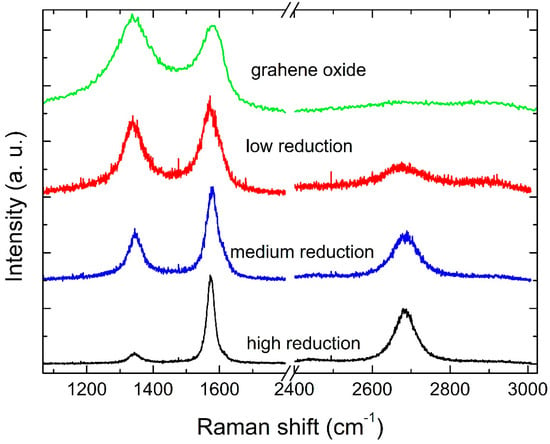
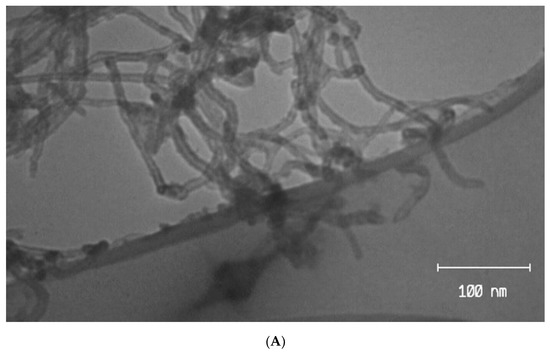
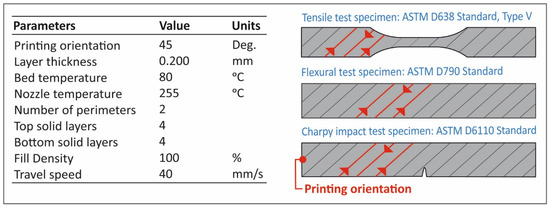
Feature Papers in the Science and Engineering of Carbons
A topical collection in C (ISSN 2311-5629).
Viewed by 145885Editors
Interests: electrochemistry; additive manufacturing; 2D material electrochemistry; sensor design and development; screen-printing and related sensor fabrication; electron transfer; sono-electrochemistry; nanoparticles
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: experimental stress mechanics; polymeric composite materials; carbon nanotube fibers; integrated and distributed structural health monitoring in composite materials; piezoresistive sensors
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
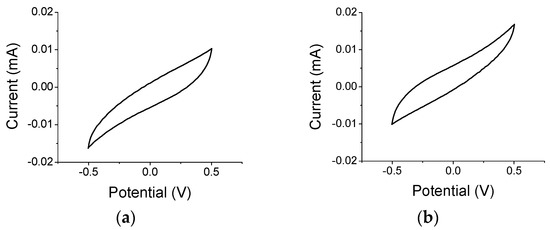
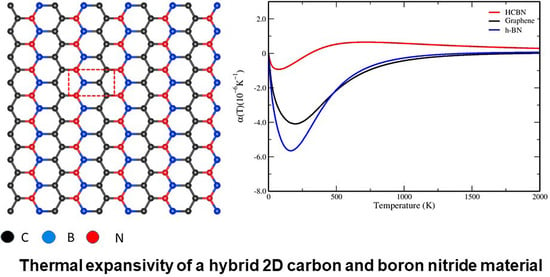
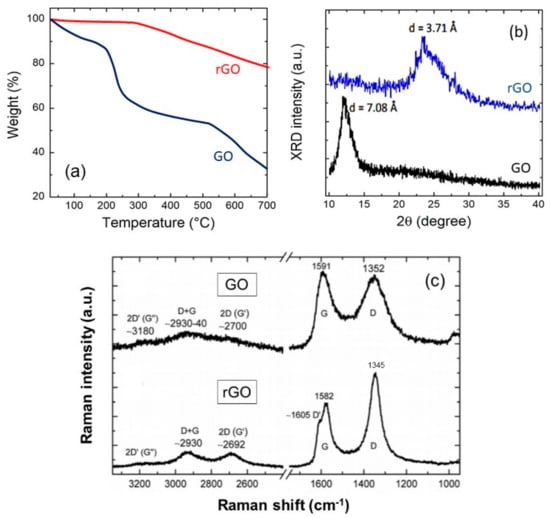
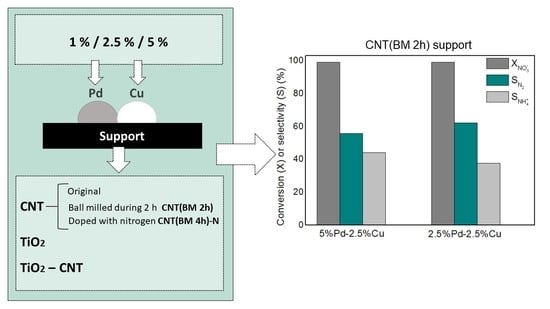
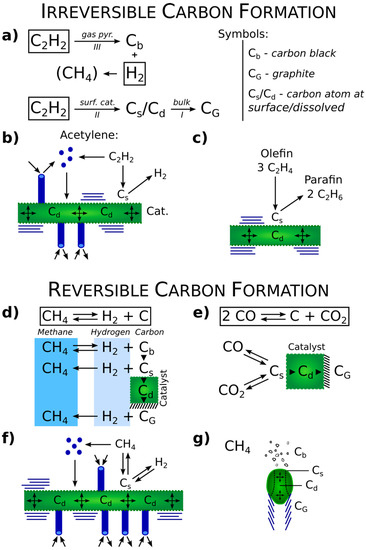
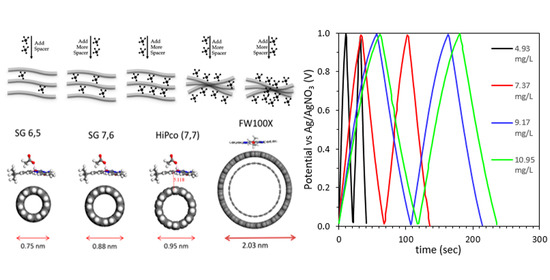
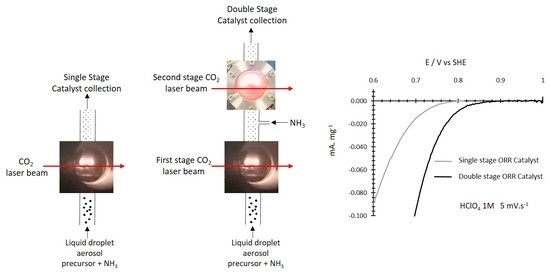
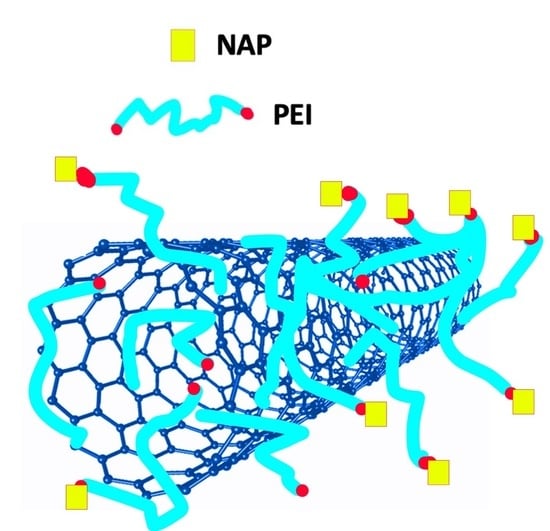
The Topical Collection “Feature Papers in the Science and Engineering of Carbons” will include high-quality research articles, short communications, and review articles about the physics, chemistry, engineering or technological applications of carbon phases and structures including graphite and pyrolytic carbon; diamond; carbon black; glassy carbon; porous carbons; graphene, fullerenes and carbon nanotubes; carbyne, sp2 and non-sp2 hybridized carbons; and carbon-carbon and other carbon composites. Since the aim of this Topical Collection is to illustrate through selected works the frontier research in this field, we encourage the editorial board members and members of the scientific community at-large to submit their works. Special areas of interest to C-Journal of Carbon Research include but are not limited to the following:
- Carbon Materials and Carbon Allotropes
- CO2 Utilization and Conversion
- Carbon Cycle, Capture and Storage
- Carbon Skeleton
- Combustion Emissions
Prof. Dr. Craig E. Banks
Prof. Dr. Jandro Abot
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. C is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.