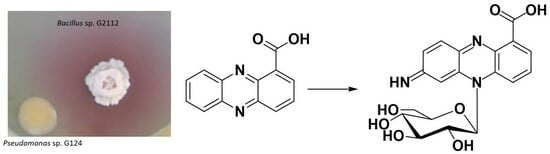
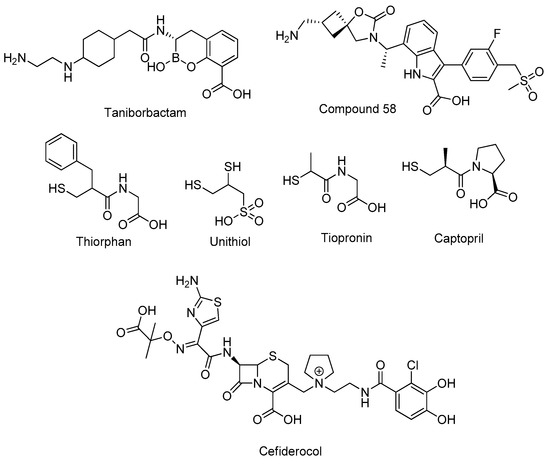
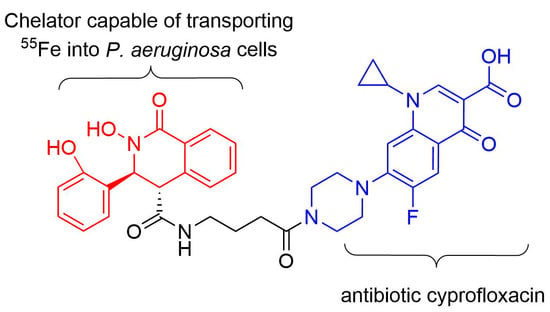
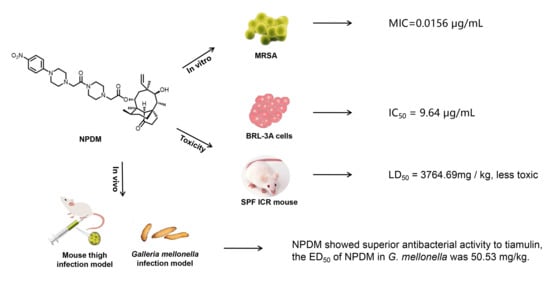
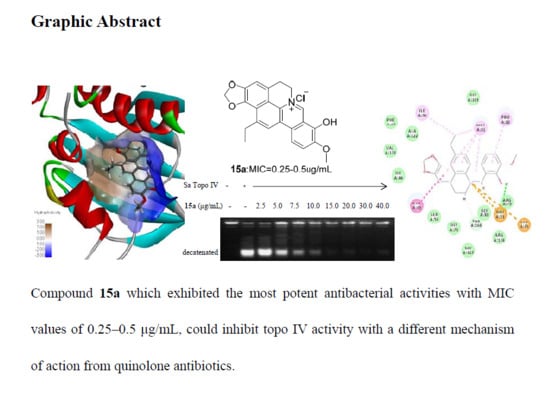
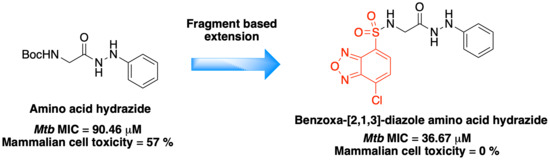
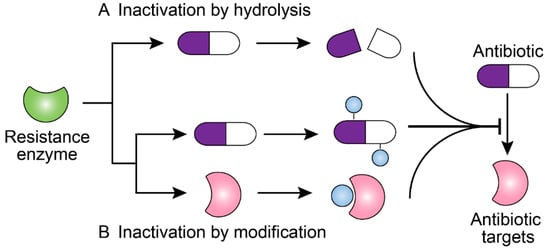
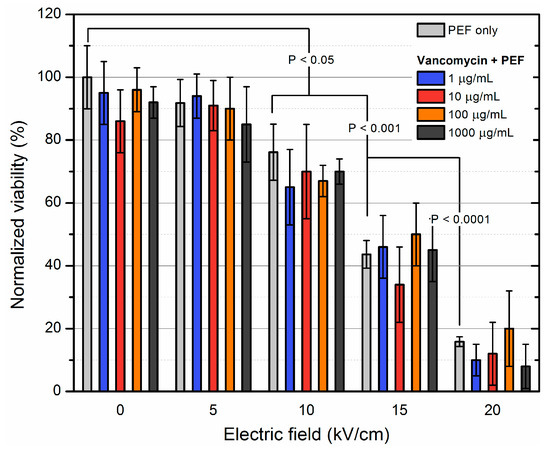
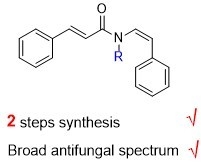
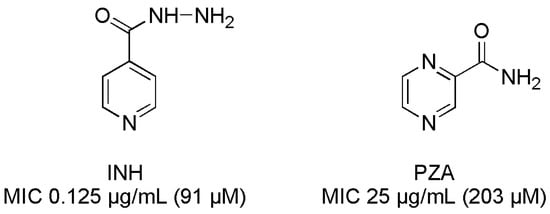
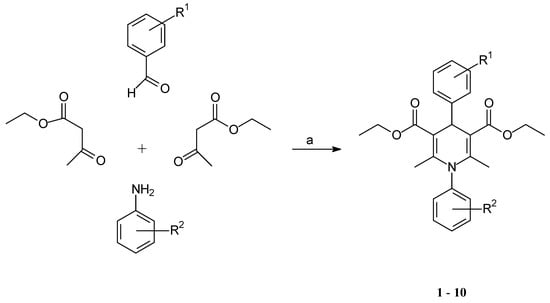
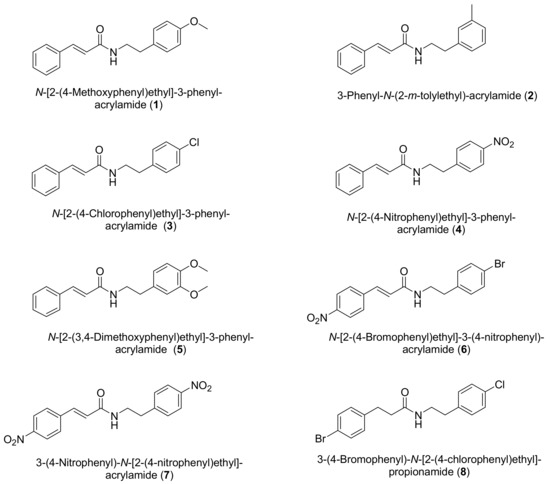
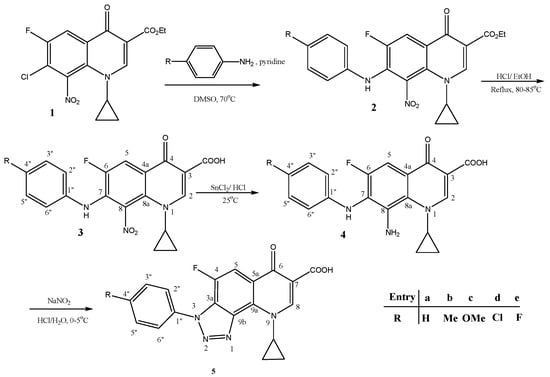
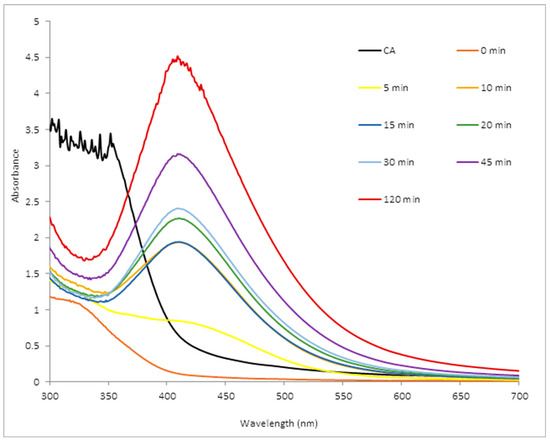
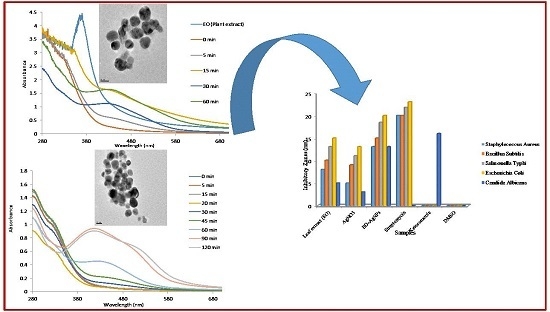
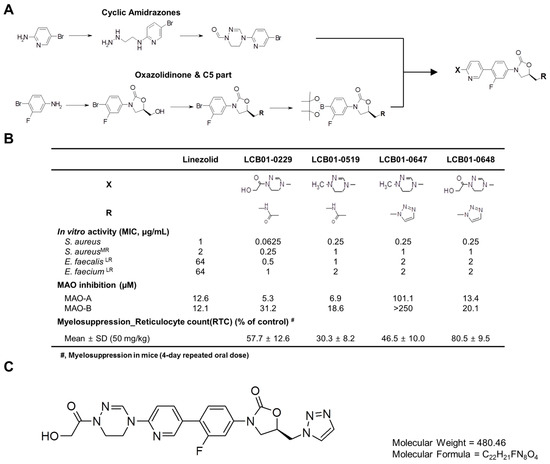
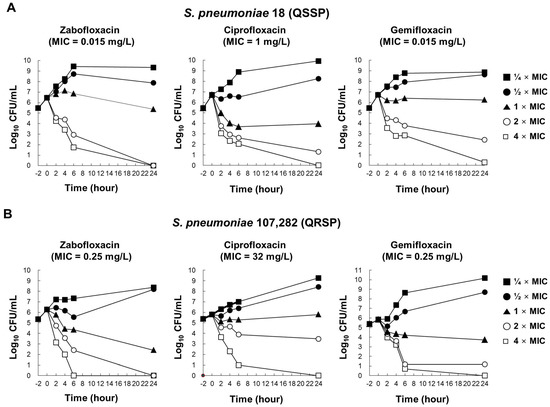
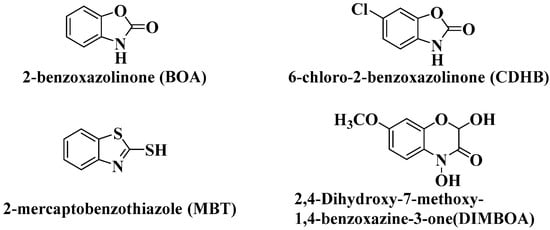
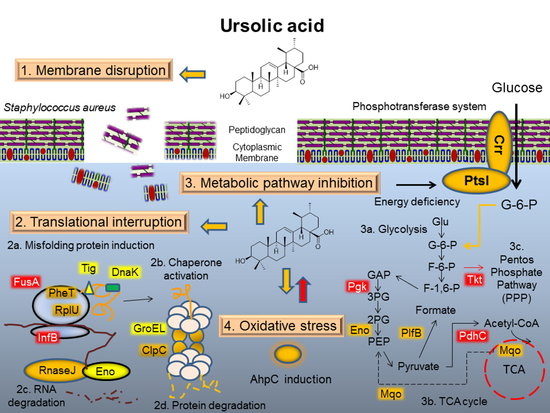
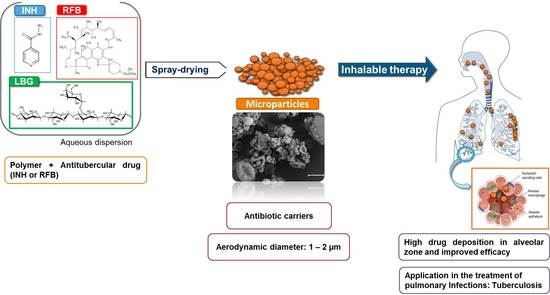
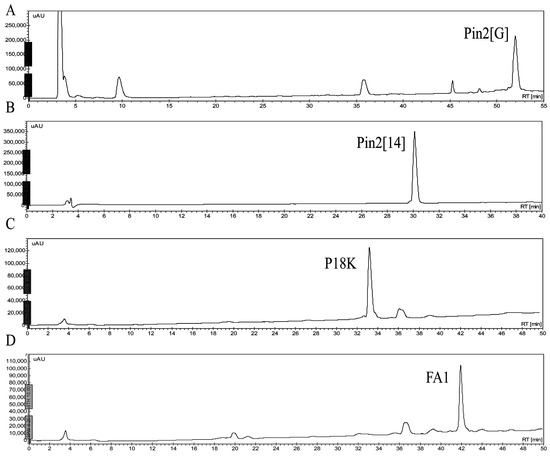
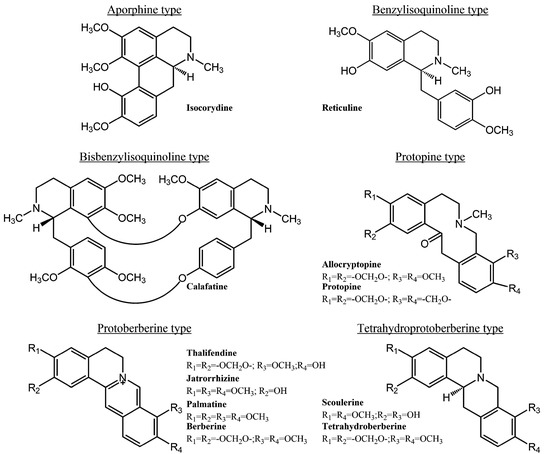
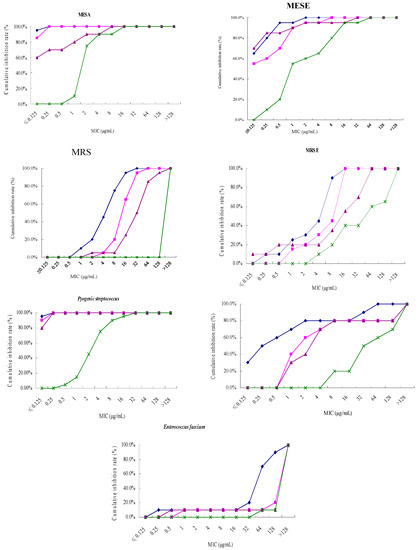
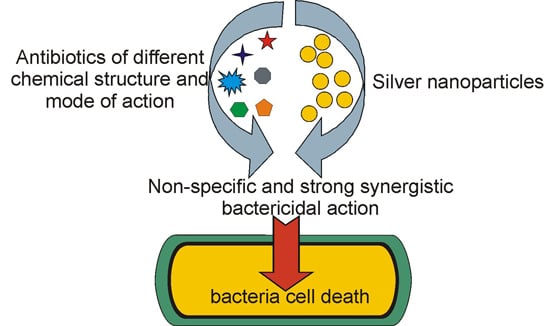
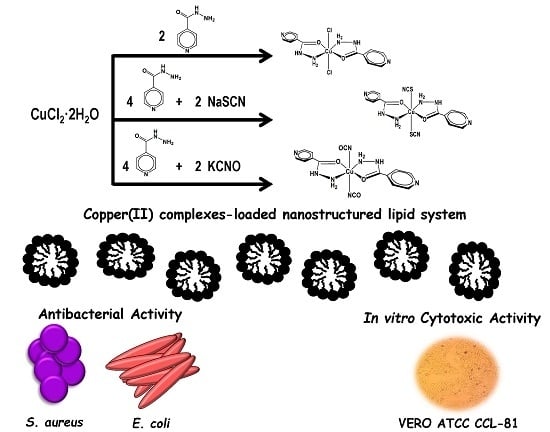
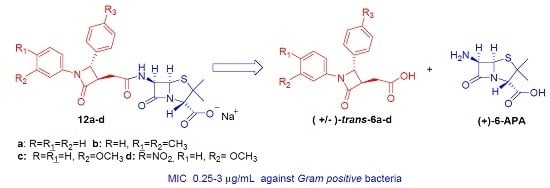
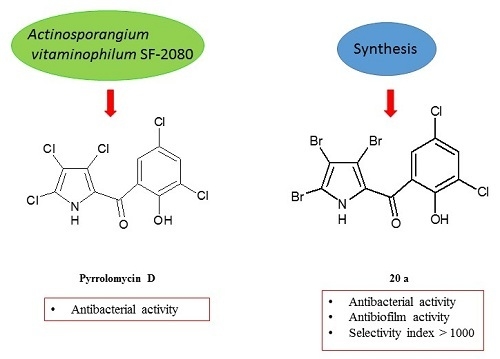
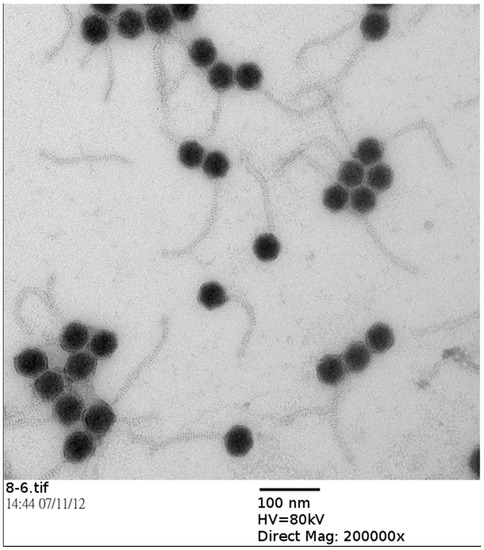
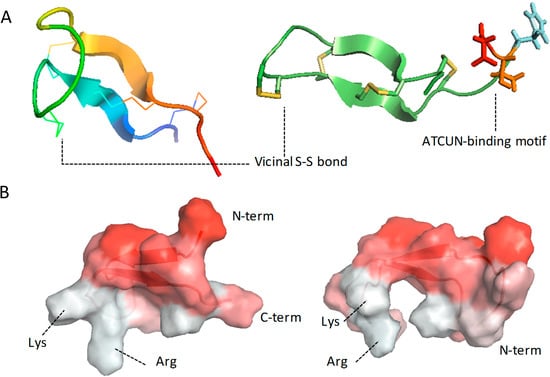
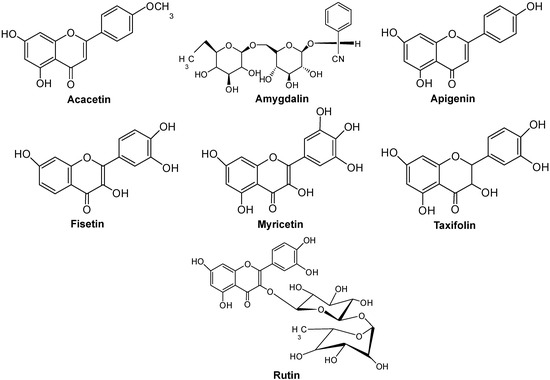
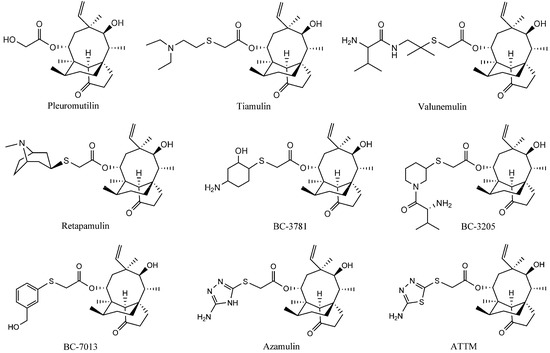
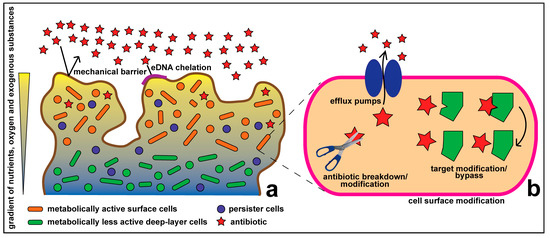
Antibiotics & Superbugs: New Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
A topical collection in Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049). This collection belongs to the section "Medicinal Chemistry".
Viewed by 684508Editor
Interests: antibiotics chemistry; biosynthesis; chemosensors and molecular probes; biocatalysis and bioinspired catalysis; hydrocarbon oxidation and C-H activation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
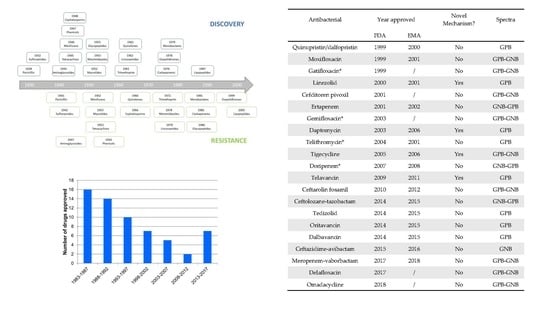
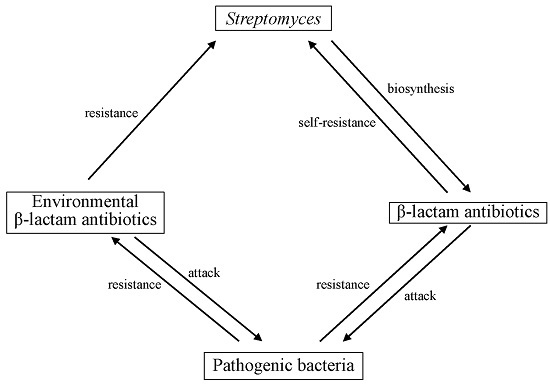
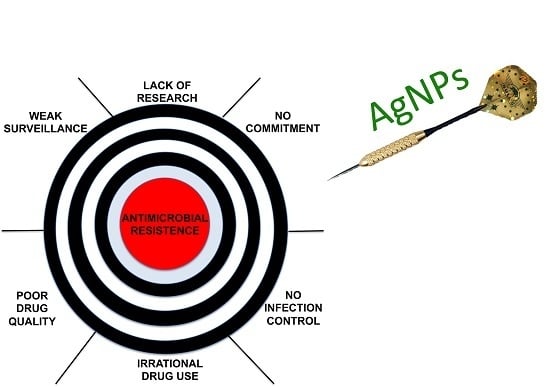
The rise of bacterial resistance to antibiotics is well documented both in the scientific literature and in the popular press. The World Health Organisation recently described antimicrobial resistance as “a problem so serious that it threatens the achievements of modern medicine.” [1] Writing in Nature, professors Mark Woolhouse (Professor of Infectious Disease Epidemiology at the University of Edinburgh) and Jeremy Farrar (Director of the Wellcome Trust) argue that in some ways, a post-antibiotic world has already arrived [2]. While Britain’s Chief Medical Officer Dame Sally Davies has called antimicrobial resistance “a threat arguably as important as climate change for the world.” [3]
The stakes are high, the pressure is mounting. This Special Issue of Molecules brings together a selection of current efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance: work that will develop new strategies and build new molecules to lead us through this crisis point and into a new ’golden age’ of antibiotics. In the words of Dame Sally Davies, “We need to work with everyone to ensure the apocalyptic scenario of widespread antimicrobial resistance does not become a reality.” [3]
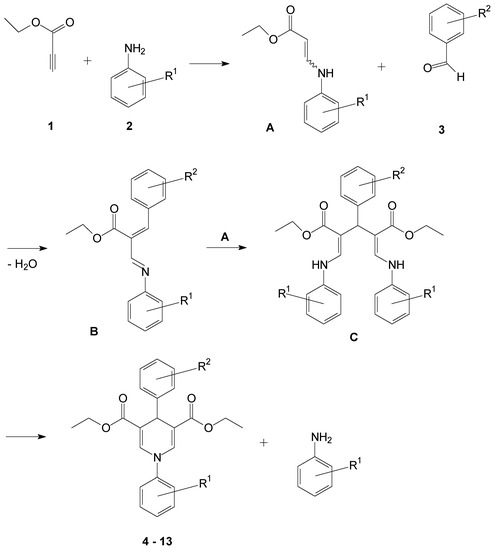
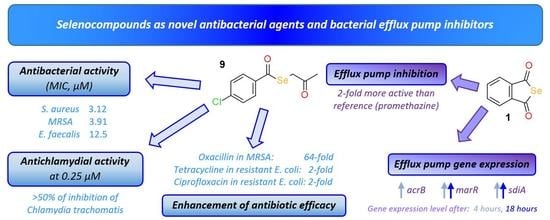
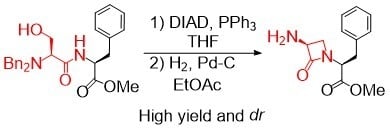
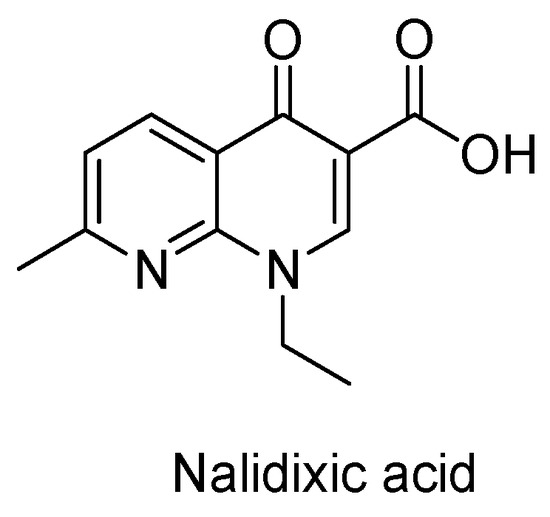
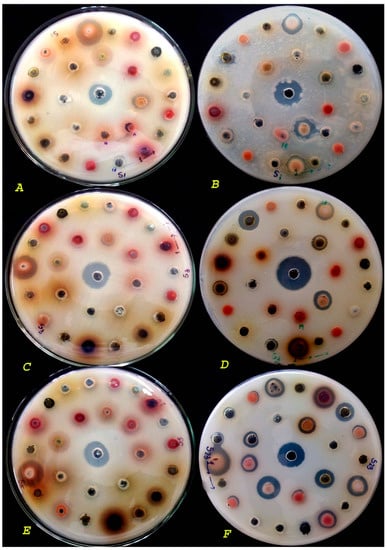
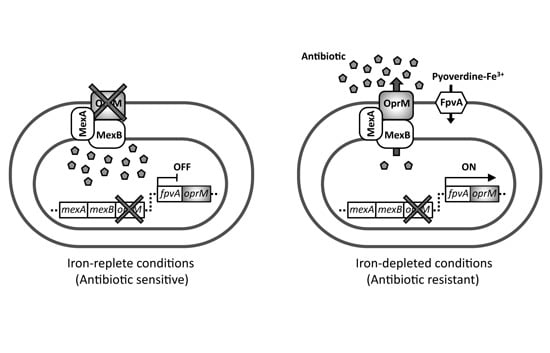
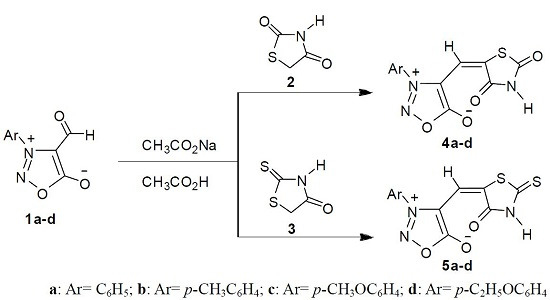
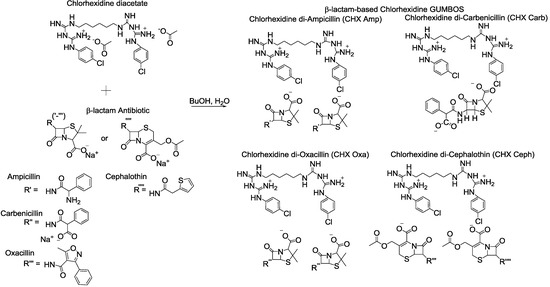
Research papers covering all areas of antibiotics chemistry are invited, from antibacterial discovery and development to the synthesis and biosynthesis of antibiotics; characterisation of resistance mechanisms and the development of strategies to combat resistance; mechanism of action studies; strategies that target quorum sensing, virulence factors or antibacterial vaccines. Review articles outlining recent developments in the field are also welcome.
- World Health Organisation, Antimicrobial resistance: Global report on surveillance 2014 (WHO 2014).
- Woolhouse, M.; Farrar, J.; Nature 509 555–557 doi: 10.1038/509555a
- Department of Health (UK), Annual Report of the Chief Medical Officer 2011: Volume Two (Department of Health 2013).
Prof. Dr. Peter J. Rutledge
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Molecules is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- antibacterials
- antimicrobial agents
- antibiotic resistance
- superbugs
- antibacterial natural products
- biosynthesis of antibiotics
- genome mining
- antibiotic drug discovery
- synthesis of antibiotics
- mechanism of action studies
- betalactamase
- quorum sensing modulators
- virulence factors
- antibacterial vaccines