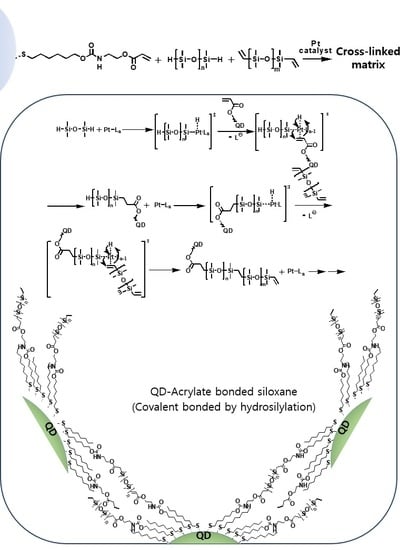
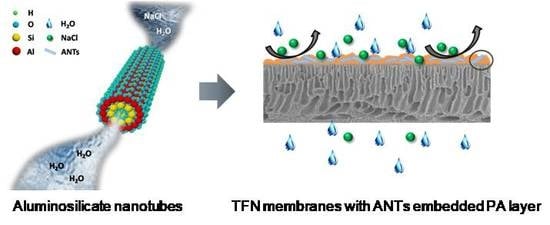
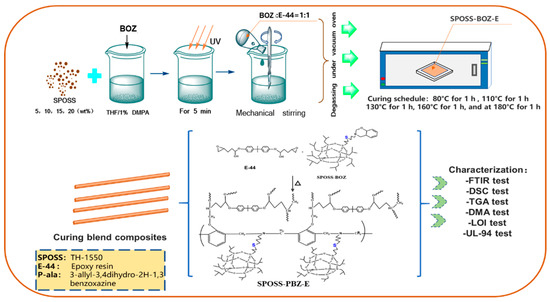
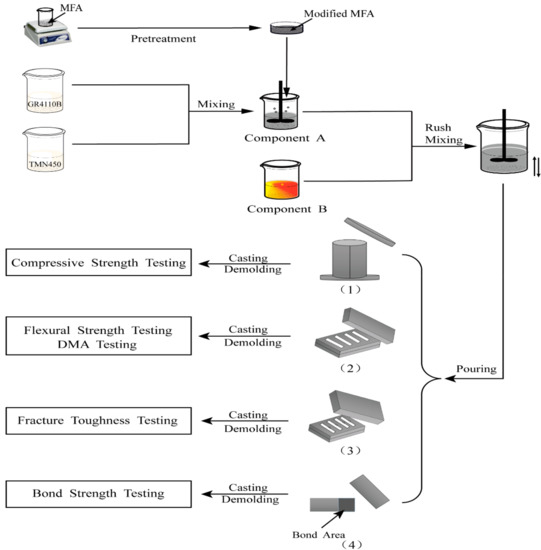
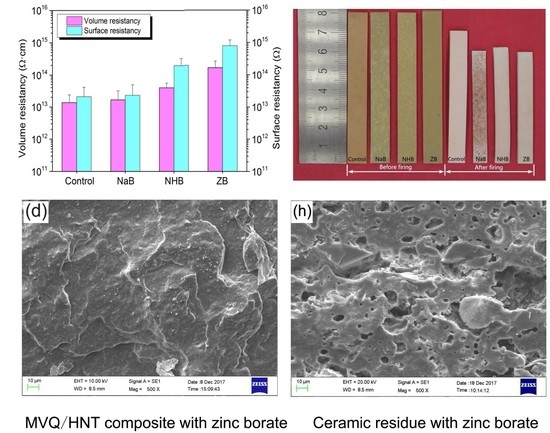
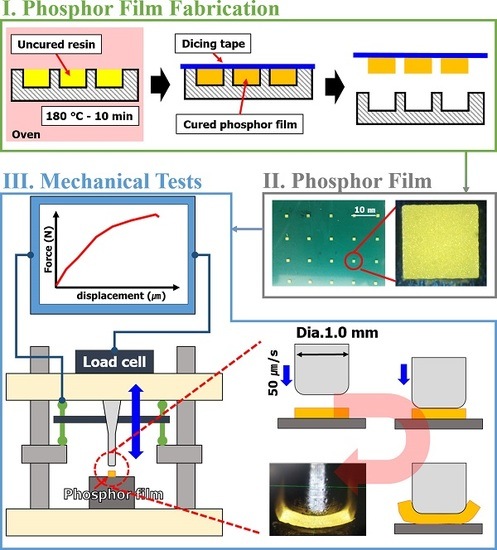
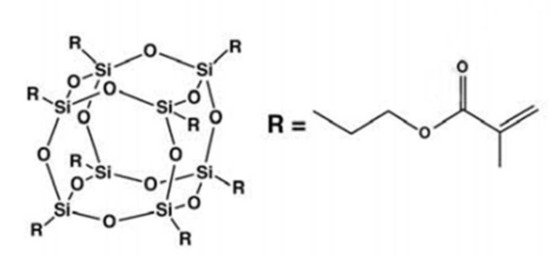
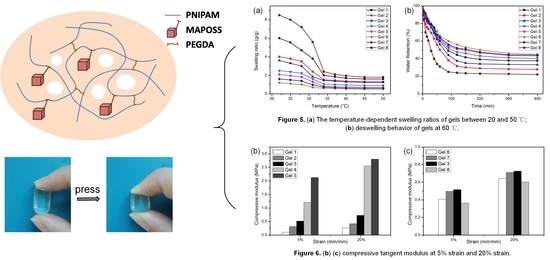
Silicon-Containing Polymeric Materials
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Polymer Chemistry".
Viewed by 492286Editor
Interests: materials; polymers; thermal properties; nanocomposites; composites
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
When thinking about a chemical element that has contributed to the technological progress over the last two centuries, carbon and all carbon-based materials immediately come to mind. By the way, especially during the last century, Silicon and its related materials follow very closely. The versatility of silicon-based materials and silicon’s abundance in the earth's crust make us sure that it will continue to play, in the years to come, a vital role in everyday life. In addition to silicones, or polysiloxanes, which have been known and manufactured for many years, silica-reinforced polymers, silsesquioxaness, and POSS-based polymers also offer a multitude of very useful consumer products. The combination of silicon and oxygen atoms with organic groups has lead to the generation of new and modified silicon-containing polymeric materials, thus providing an exciting mixture of properties and offering a wide spectrum of practical applications. We are interested in articles that explore silicon-containing polymeric materials and their applications.
Prof. Dr. Ignazio Blanco
Collection Editor
Related Special Issues
- POSS-Based Polymers in Polymers (19 articles - displayed below)
- Siloxane-Based Polymers in Polymers (14 articles - displayed below)
- Silsesquioxane (POSS) Polymers, Copolymers and Nanoparticles in Polymers (9 articles - displayed below)
- Silicon-Based Polymers and Materials in Polymers (8 articles - displayed below)